From training KPIs to learning KPIs
Effectiveness in learning processes through predictive analytics and data-based tutoring actions
A joint work

AI-ML expert
I’m here and
I’ll do my best!

Learning Expert
She’s not here!

Indexes Expert
She’s not here!
Introduction
Early Identification of Critical Issues
- A model utilizing statistical indexes and predictability in the LMS platform
- Statistical aggregated indexes system built upon LMS data
- Identifying potential critical issues by analyzing design and organizational inconsistencies within the indexes (data derived).
- Also through predictive AI (ML) system
- Highlighting these issues early for:
- proactive actions to be taken
- optimizing the performance of the training system
A Model of Analysis of the Tracking Data
- From the experiences of digital learning operators
- A tool capable of synthesizing all aspects of training
- A Macro Index of Performance (MIP) as a weighted aggregation of seven sub-indexes:
- Results (IR)
- Study Pace (ISP)
- Course Structure (ICS)
- Computer Adequacy (ICA)
- Community Participation (ICP)
- Educational Tutoring (IET)
- Process Tutoring (IPT)
- Weighted aggregation by quantifying company experience with an ad hoc AHP Bayesian model (Analytic Hierarchy Process)
A Model of Analysis of the Tracking Data
- The sub-indexes are a weighted aggregation of different normalized variables
- Normalized means \(\in[0,100]\)
- Thus, every variabes, the seven sub-indexes and the MIP \(\in[0,100]\)
Macro Index of Performance (MIP)
- A Unified Analysis Model for Training
- Enables Comparison and Discrimination Between Course Methods (online, classroom, blended)
- Guides Tutors in Differentiated Intervention Methods
- It can discriminate different experiences and indicate the expected outcomes based on similar patterns
A Model of Criticalities
Experiments with LearnalyzeR
- Using feedback from our first experiments
- Analysis of critical situations using the MIP and sub-indexes patterns.
- Also providing tutors with potential preventive intervention strategies.
A first course criticality definition
The behavior of a non-neglecting part of participants that leads to a course experience that does not satisfy their fruition, participation, times, and performance needs.
Criticalities Recognition (a second definition)
- Different criticalities
- Criticalities from already known patterns using only course data.
- Calculated during the course, and the course is already critical when observed.
- Predictive patterns of criticality with respect to historical behavior.
- Calculated during the course, and the course is not critical when observed.
- Distorted use of times and verification of didactal units at risk.
- Calculated only at the end of each unit, and then, it can be summarized only at the end of the course.
Three Classes of Criticalities
- From previous definition, we identified three classes of criticalities:
- Participation (CPA), the access and use of course materials using sub-indexes variables
- Performance (CPE), the effectiveness of the training course according to the training plan using a Bayesian regressor to forecasting the final MIP
- Structure(CS), criticality in using educational resources with excessive use of time and expenditure of organizational costs.
- We defined it mixing the expertise of tutors and LMS data (MIP, sub-indexes, variables)
Participation (CPA)
| C_PA TYPE | CONDITION | PROBLEM | INTERVENTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Elapsed available time between 15% and 25%, not less than 75% of participants have a use time of less than 25% | Reduced number of users who have started | Reminder to Start |
| B | Elapsed available time between 25% and 50%, not less than 50% of participants have a use time less than 50% | Reduced number of users with significant progress | Reminder to Study |
| C | Elapsed available time between 50% and 75%, not less than 25% of participants have a use time of less than 25% | Risk of drop out | Reminder to Recover |
Participation (CPA)
| C_PA TYPE | CONDITION | PROBLEM | INTERVENTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| D | Elapsed available time over 75%, not less than 25% of the participants have a use time less than 75% | Users with completing difficulty | Reminder to Complete |
| X | Available time ended, at least 10% of users did not complete the course | Incomplete course | Extension or Recovery |
Performance (CPE)
| C_PE TYPE | CONDITION | PROBLEM | INTERVENTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Elapsed available time between 20% and 40%, less than 20% of participants with MIP forecast at the end of the course > threshold value | Inadequate study behaviour | Encourage effective study |
| B | Elapsed available time between 40% and 75%, less than 50% of participants with MIP forecast at the end of the course > threshold value | Study behavior at risk of ineffectiveness | Make organizational proposals and give advice |
Performance (CPE)
| C_PE TYPE | CONDITION | PROBLEM | INTERVENTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | Elapsed available time between 75% and 80%, less than 50% of participants with MIP forecast at the end of the course > threshold value | Highly risky study behaviour | Give organizational proposals, re-registrations / extensions |
| X | Available time ended, at least 10% of users with end-of-course MIP below the threshold | Incomplete course | Extension or Recovery |
Structure (CS)
| C_S TYPE | CONDITION | PROBLEM | INTERVENTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| Z | At least 50% of the participants have fruition times greater than twice the time provided in the course design | Inconsistent use of time, educational resources criticality | Review course rules and/or design |
Data based tutoring Interventions
Data based tutoring Interventions
- Using the data-based criticality structure previously defined
- We can define a precise structure of inteventions
- We will give few examples
Participation Criticality Type C
- Recover lagging participants
- Identify cases of proper abandonment
- Verify results and IT adequacy sub-indices
- Provide study plan and operational advice to help them catch up
- Report the importance of respecting the indicated study times for certificates and certifications
Performance Criticality Type Z
- Identify lagging users, and check their actual completion status and the sub-indexes
- Monitor participants’ progress to identify those who are struggling
- Check the sub-indexes to determine areas where participants may need extra support
Structure Criticality Type B
- Verify organizational times and conditions for the schedulation’s adequacy with the structure of the course and the expected complexity
- Verify the incidence of technical factors
Identifying Course Criticalities Using LearnalyzeR
Visualizing the Macro Index of Performance (MIP)
- The first step in using LearnalyzeR involves visualizing the median value of the Macro Index of Performance (MIP) by placing a colored dot over it.
- This quick assessment helps to understand course performance (derived from previous courses evaluation by tutors):
- Gray: MIP is not calculable
- Red: Inadequate performance with many critical elements; MIP value < 50
- Orange: Quite adequate performance with few critical elements; MIP value ≥ 50 and < 70
- Yellow: Good performance with areas for improvement; MIP value ≥ 70 and < 80
- Green: Excellent performance; MIP value ≥ 80
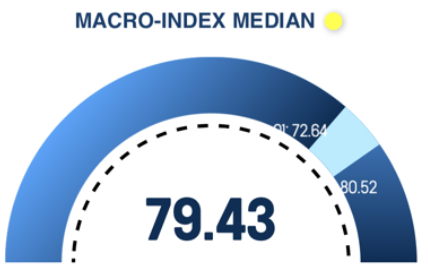
Course Criticality Examples
- In this example, LearnalyzeR is used to identify the causes of course criticalities in a public administration course.
- By visualizing MIP, sub-indices, and variables that make up these indices, we can understand the symptoms (diagnosis) and prepare targeted tutoring actions (therapy).
- The focus is on showcasing the logic of analysis.
Different User Populations on the Same Courses
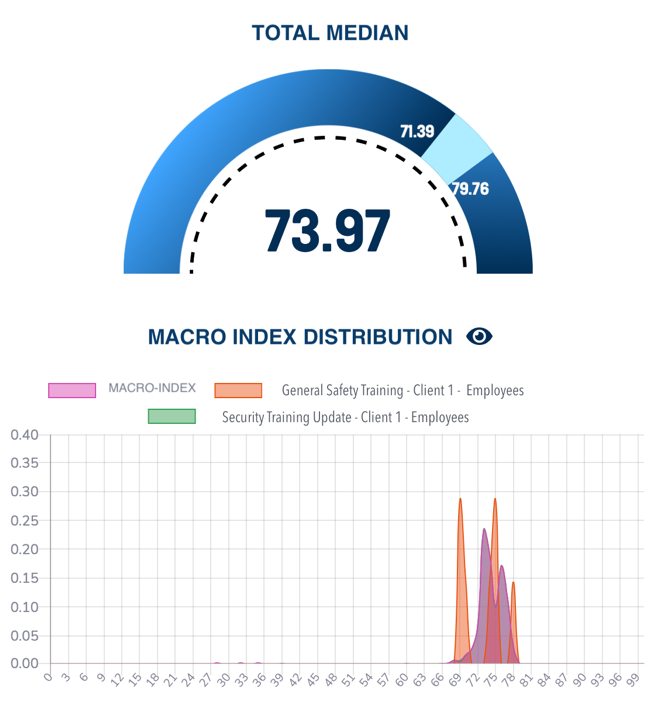
- Median MIP values: Population 1 - 74; Population 2 - 65
- Population 1 showed a homogeneous behavior in the MIP range between 69 and 78
- In contrast, population 2 had a more significant variability of study behavior with a long queue on the left (towards low values of MIP up to 27)
- Study behavior variability: Greater in population 2, especially for General Training and Updating
- Engagement actions needed: based on participation criticality of type d
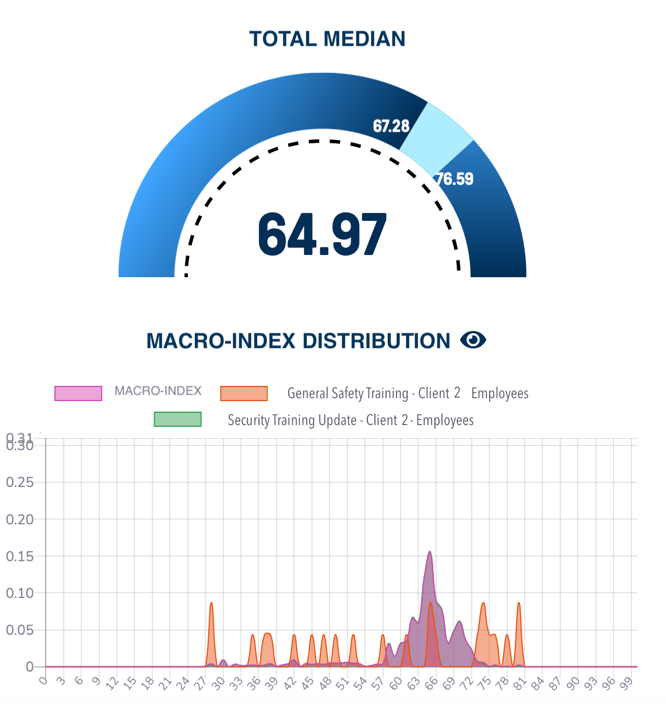
Detailed Analysis of Criticality
- From another edition
- Participation criticality: Type d, with sub-index Results having a median value of 50
- Study behavior problems: Users had good IT adequacy but struggled with open sessions (variable open sessions is 60)
- Engagement actions needed: based on combination of structure criticality and study pace issues
- Forecasted MIP range at the end of the course: 70.6 - 85.8
- Expected dropout rate at course completion: 50%
- Macro-index forecasts are above the threshold, but not all users will complete courses
Systematic Approach to Tutoring
Impact of Criticality Detection and Data-Driven Tutoring Systems
- A systematic approach to criticality detection ensures a rigorous procedure for analyzing behaviors and results, providing insights into course and participant performance.
- Adopting a data-driven tutoring system allows effective modulation and analysis of the impact on effectiveness indicators.
- By focusing on predictability and systematic analysis, tutors can intervene selectively in high-risk situations, tailoring communication to individual needs.
- This data-based intervention system enables tutors to evaluate their actions’ effectiveness, guiding them towards the best solution for individual critical issues.
- Our criticality model is explainable
Future Integration Features
- Include tutoring actions in macro-index track, evaluating actual and systematic tutoring impacts on results
- Study sub-index evaluation thresholds to better decode critical areas
- Integrating extra measures for Results category with focus on:
- Learning assessment analysis
- Observed results/work performance
- Improve satisfaction measurement through NLP analysis in didactic tutoring category
- Add AI agent-based actions through an explainable framework (XAI)
Questions?

baltig.cnr.it/mario-santoro

learnalyzer.it

learnalyzer.it
Appendix
A Criticalities detecting system
- to support the intervention of tutors day by day through
- predictive systems
- analysis of participation behaviors,
- redesign of courses.
Participation Criticality Type A
- Verify login information
- Check work contingencies
- Verify IT adequacy sub-index
- Verify results and pace of study sub-indices
- Assess engagement and motivation
Participation Criticality Type B
- Send reminders to inactive participants
- Motivate participation for those who have started
- Remind everyone of times and deadlines
- Verify IT adequacy sub-index and study times
Participation Criticality Type D
- Communicate risk of non-completion
- Verify problems encountered
- Highlight a possible study plan to recover and complete the course
- Provide study plan and operational advice to help them catch up
- Report the importance of respecting the indicated study times for certificates and certifications
Structure Criticality Type A
- Act on people by remembering tips for effective and productive study
- Refer to the tutor for personalized advice
- Encourage participants to adopt good study habits
- Remembering tips for effective and productive study can include:
- Time management techniques
- Note-taking strategies
- Active learning methods
Structure Criticality Type C
- Identify lagging users, and check their actual completion status and the sub-indexes
- Monitor participants’ progress to identify those who are struggling
- Check the sub-indexes to determine areas where participants may need extra support
Structure Criticality Type X
- The course is over. Among the course completed participants, more than 10% have a MIP of less than 70 (empirically defined)
- Analyze the index and sub sub-indexes data to identify areas where participants struggled
- Use this information to improve future courses and interventions
